If you are searching for a better understanding of What is BPMS? and why it is vital for organizations, this article is just for you.
In this article, we will introduce Business Process Management (BPM), BPMS software, their differences, capabilities, advantages, applications, and even challenges. We will also help you clarify the path to choosing and implementing BPMS so that you can perform more successfully in today's business competition.
What is BPMS?
BPMS or Business Process Management System is the Persian term for "Business Process Management System." This BPMS software is a tool for designing, executing, monitoring, and continuously improving organizational processes.
What does BPMS stand for?
BPMS stands for Business Process Management System, which directly translates to "Business Process Management System."
By using BPMS software, organizations can:
- Standardize and automate their processes.
- Make decisions based on real data.
- Significantly increase efficiency and agility.
Difference Between BPM and BPMS
BPM or Business Process Management is a management approach and framework that focuses on continuous process improvement. In contrast, BPMS is software and a technological platform that enables the practical implementation of this approach.
| Comparison | BPM | BPMS |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Management approach | Software and tools |
| Goal | Continuous process improvement | Practical implementation and automation |
| Focus | Strategy and design | Implementation and execution |
| Outcome | Culture of improvement in the organization | Digital transformation tool |
| In simple terms | Like a roadmap | A vehicle that drives you along that path |
| Summary | Mindset and strategy for process management | Tool for implementing and automating BPM |
Why is BPMS essential for organizations?
Today, organizations operate in a competitive environment that requires speed, accuracy, and agility. BPMS helps organizations to:
- Standardize and automate their workflows.
- Reduce costs and human errors.
- Increase transparency and accountability.
- Implement continuous improvement based on real data.
For example, in an insurance company, using BPMS can reduce the time taken to process claims from several days to just a few hours.
The role of BPMS in increasing productivity
Many organizations still perform repetitive and manual tasks with human resources. This not only consumes time but also increases the likelihood of human errors. BPMS addresses this issue by automating processes. For instance, in a service company, if the customer request registration process is done manually, it might take several days. However, with BPMS, these requests are automatically referred to the relevant expert and reviewed the same day.
The importance of BPMS in digital transformation
Digital transformation is not possible without process management. BPMS acts as a bridge between digital transformation strategies and their practical implementation. This system helps not only to digitize processes but also to combine them with new technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA).
Advantages of BPMS
The benefits of using BPMS software are quite extensive. Some of the most important advantages include:
Reduction of costs and human errors
By automating repetitive tasks, organizations significantly reduce costs associated with rework, errors, and wasted time.
Improving customer experience
Today's customers seek speed and quality. BPMS allows processes to be executed faster and more accurately, resulting in increased customer satisfaction.
Flexibility and agility of the organization
The market is changing rapidly, and organizations must be ready to respond swiftly. BPMS provides the ability to change and redesign processes in the shortest time.
Reporting and data-driven decision-making
One of the most valuable features of BPMS is the ability to analyze data and generate reports. Managers can make more informed decisions by viewing key performance indicators (KPI) in real-time.
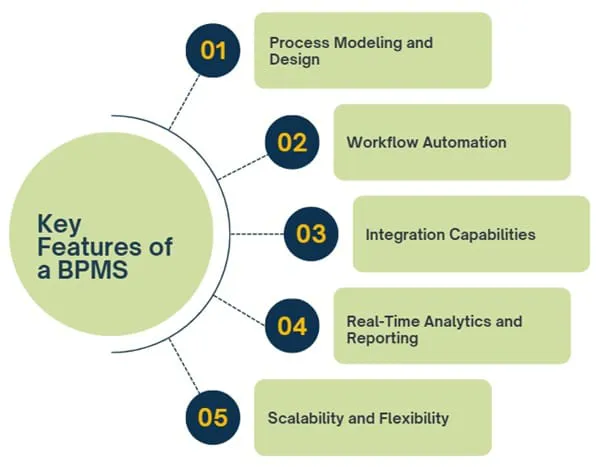
BPMS software and its capabilities
A standard BPMS software includes the following capabilities:
Process modeling with BPMN
BPMN is a visual language for designing processes. With this tool, even those with little technical knowledge can design and understand workflows.
Automating workflows
BPMS automatically distributes tasks among employees and progresses work according to the correct order.
Monitoring and tracking KPIs
Managers can monitor process performance in real-time and take corrective actions as needed.
Integration with ERP, CRM, and APIs
One of the important features of BPMS is that it easily integrates with other organizational systems such as ERP, CRM, or even in-house software.
Task management and team collaboration
Employees can view and track their tasks through interactive dashboards. This capability enhances team collaboration and increases organizational productivity.
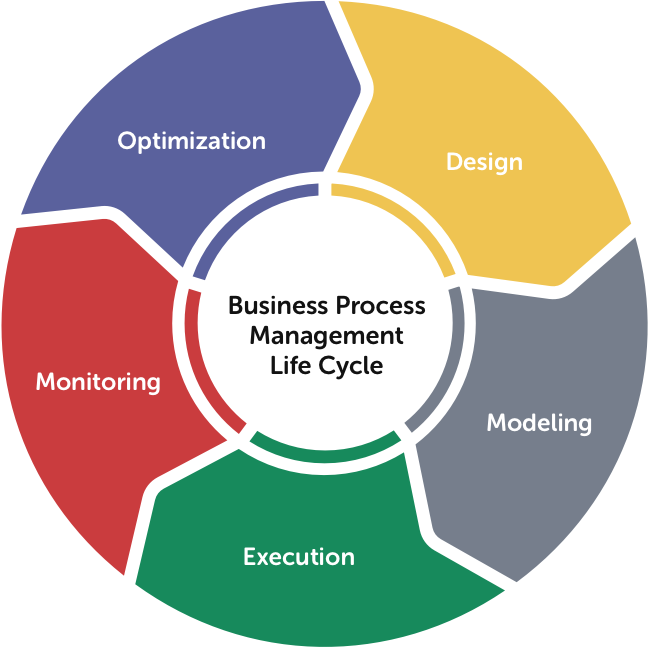
How does BPMS work? (BPMS lifecycle)
The BPMS lifecycle includes several main stages that are continuously repeated:
1. Process analysis and documentation
Initially, the organization's key processes are identified and documented.
2. Modeling and design
Processes are graphically designed using the BPMN standard.
3. Implementation in software
The designed process is integrated into the BPMS software, and automation begins.
4. Monitoring and continuous improvement
Process performance is monitored, and weaknesses are identified and corrected.
This cycle does not occur just once, but rather it is continuously repeated so that the organization is always improving.
Comparing BPMS with ERP and CRM
When it comes to enterprise software, three common names always come to mind: BPMS, CRM, and ERP. Each serves different goals, but together they can form the backbone of a digital organization.
Fundamental Differences
-
BPMS (Business Process Management System):
The main focus of BPMS is on managing, automating, and improving processes. This software helps workflows be executed faster, more transparently, and with fewer errors. -
CRM (Customer Relationship Management):
CRM focuses on managing customer relationships. Its aim is to increase sales, improve after-sales services, and enhance customer experience. -
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning):
ERP is designed for managing organizational resources, from accounting and finance to inventory, production, and human resources. The aim of ERP is better coordination among different organizational units.

Similarities
-
All three systems work with organizational data.
-
Their common goal is to improve productivity and enhance organizational performance.
-
They all have the capability for reporting and data analysis, but in different domains.
Synergy and Complementarity
BPMS, CRM, and ERP are not rivals to each other but rather complement each other. For example:
-
A customer order starts through CRM.
-
Order processing and approval are managed and guided by BPMS.
-
Inventory control and resource planning are managed through ERP.
This collaboration ensures that organizations have a fully digital and integrated cycle; a cycle that keeps both customers satisfied, optimizes resource management, and enhances processes efficiency.
Challenges and limitations of BPMS
Although BPMS has many advantages, its implementation is not without challenges. Some obstacles organizations may experience include:
Employee resistance
Change is always accompanied by resistance. Employees may feel concern towards automation and changes in processes, as they think they might be replaced or need to learn new skills.
Implementation cost and time
Implementing BPMS requires an initial investment. Additionally, it might take a longer time to fully adapt the organization to the new processes.
Need for training and cultural change
BPMS is not just a tool; it represents a shift in organizational culture. Without proper training and cultural change, project success may diminish.
Criteria for selecting the best BPMS software
Choosing BPMS software is not a small decision. If the suitable software is not selected, the entire project may result in failure. Key selection criteria include:
Simplicity and user-friendliness
BPMS software should be designed in such a way that ordinary users can use it without complex technical knowledge.
Flexibility and scalability
The needs of organizations change over time. BPMS software should have the capability for growth and customization.
Security and integrity
Given that BPMS manages sensitive organizational data, security is one of the main selection criteria. Additionally, the ability to connect to other systems (like ERP and CRM) is highly important.
📌 Always request a demo before purchasing BPMS software to ensure that the software aligns with the needs of your organization.
Examples of BPMS applications in various industries
One of the best ways to understand the value of BPMS is to observe its application in various industries.
Banking and Financial Services
In banks, BPMS can speed up loan issuance. Instead of manual verification of documents, the automated system checks the documents and, if complete, sends the case to the next stage. This reduces the customer waiting time by half.
Insurance
In the insurance sector, reviewing claims is one of the complex processes. BPMS automates this process, ensuring that customers receive their compensation faster.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
BPMS can enhance coordination between supply, manufacturing, and distribution. For instance, when the inventory of raw materials is low, the system automatically registers a new order.
Government and Public Services
Governments can simplify the issuance of licenses or citizen services with BPMS. This not only creates transparency but also enhances citizen satisfaction.

Examples of Dynamic Solution BPMS projects
One of the main differences of Dynamic Solution from many competitors is our practical experience in implementing real BPMS projects for large and national organizations. These projects not only demonstrate our technical capability but also prove the significant changes that BPMS can create in practice.
🔹 Smart Service One Stop Window of the Ministry of Roads and Urban Development
In this project, the main goal was to integrate and digitize the services of the Ministry of Roads. Dynamic Solution used BPMS to organize complex intelligent service processes and significantly increase the speed of service delivery.
👈Details Smart Service One Stop Window Project of the Ministry of Roads and Urban Development
🔹 Monitoring and Evaluation System of Iran University of Medical Sciences
This project focused on improving performance monitoring and reporting transparency. BPMS significantly reduced the time needed for evaluation and supervision, enabling faster decision-making for university managers.
👈Details Monitoring and Evaluation System Project of Iran University of Medical Sciences
🔹 Business Intelligence of Rail Seir Kowsar
In this project, BPMS was combined with Business Intelligence (BI) to provide more accurate information and analytical reports to the managers of Rail Seir Kowsar. This led to better decision-making and overall improvement in organizational performance.
👈Details Business Intelligence Project of Rail Seir Kowsar
🔹 Contract Management and Assemblies Oversight System
The main goal of this project was integrated management of contracts and corporate assemblies. Dynamic Solution, using BPMS, was able to simplify complex processes, create transparency in contract management, and provide managers with better oversight.
👈Details Contract Management and Assemblies Oversight System Project of the Ministry of Roads and Urban Development
The future of BPMS and its role in artificial intelligence
BPMS is evolving, and new technologies are making it smarter.
Combining BPMS with RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) helps BPMS automate fully manual tasks such as data entry or document verification.
Using artificial intelligence in decision-making
Artificial intelligence in BPMS can analyze data and provide suggestions for improvement. For example, the system can identify a stage of the process that is causing delays and suggest a solution to fix it.
Summary
Now that you understand what BPMS is and what benefits it has for organizations, you can start your digital transformation and productivity increase journey by selecting appropriate BPMS software. It is recommended to start with a key process and gradually cover the entire organization by repeating the improvement cycle.
For further reading, you can refer to reliable international sources like Gartner.
Frequently Asked Questions
Business Process Management (BPM or BPMS) systems are tools that help organizations optimize their processes and increase the efficiency, transparency, and flexibility of operations. These systems enable integrated and efficient process management through the use of organizational automation and workflow engines.
-
Increasing efficiency and reducing errors: By simplifying and automating time-consuming and repetitive processes, organizations can reduce errors and enhance overall efficiency.
-
Better coordination between departments: Processes are executed seamlessly, and interaction between teams improves.
-
Standardization and quality control: Processes are defined based on standards, allowing for quality monitoring and the implementation of necessary controls.
-
Performance measurement: By setting KPIs, the performance of processes can be measured and analyzed.
-
Organizational flexibility: The ability to quickly change processes based on market needs or internal changes is provided.
The business process management cycle usually includes the following steps:
- Design
- Model
- Execute
- Monitor
- Optimize
It depends on the organization's scale and the complexity of the processes. However, in the long run, the savings resulting from it are usually several times the initial cost.
Yes, most BPMS software have the ability to connect to ERP, CRM, and other internal systems.