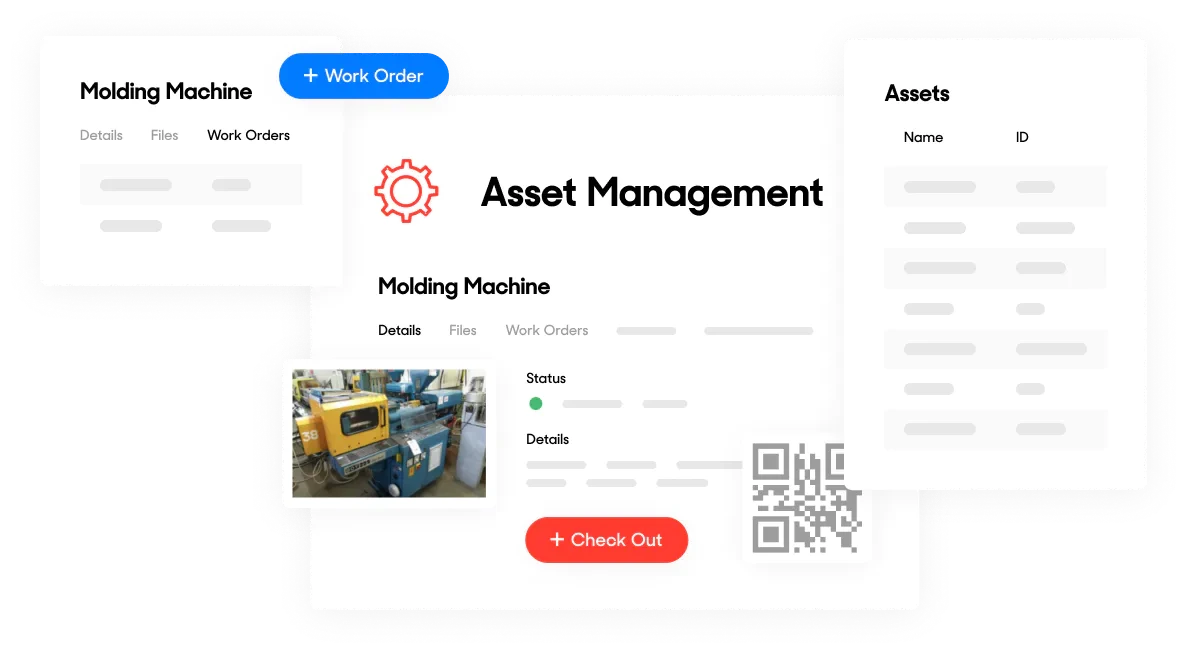
The Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) is a computerized management system used to monitor, plan, execute, and record maintenance activities for machinery. These systems utilize information technology and software tools to improve performance and optimize maintenance processes. CMMS is defined as a comprehensive system for asset and equipment management, which includes data collection, analysis, and decision-making based on real information.
The CMMS consists of the following components:
-
Equipment Information Management:
These components are used to register information related to machinery, including technical specifications, maintenance history, required parts, and other relevant information. -
Planning and Scheduling:
This part of the system is used to plan maintenance activities based on a specific schedule and includes periodic maintenance planning, parts replacement, regular inspections, and other maintenance-related activities. -
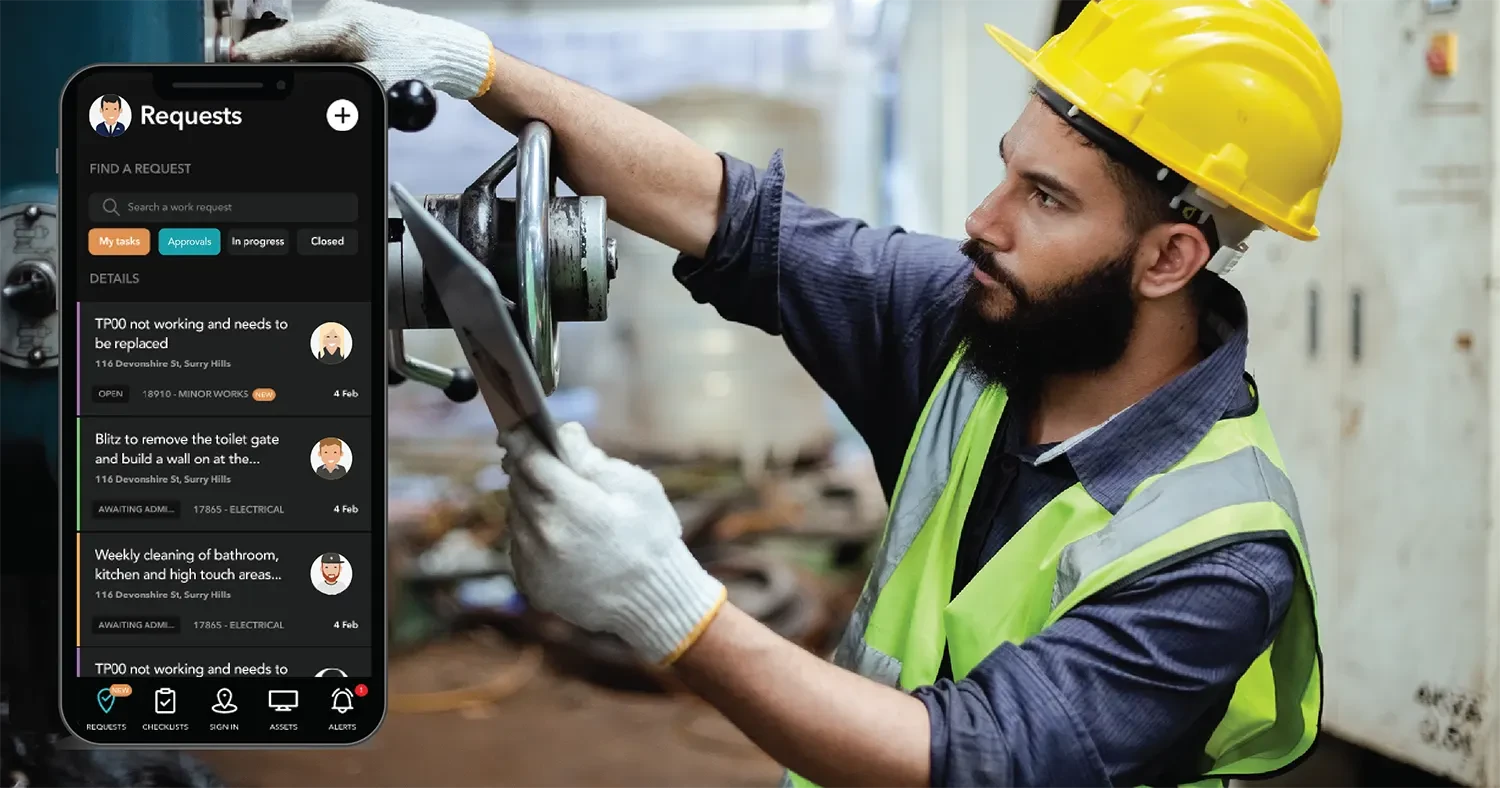
Fault and Request Registration:
In this section, users can register faults, problems, or requests regarding the machinery. This information is referred to the maintenance team to track requests and carry out necessary operations. -
Activity Tracking and Execution:
This section includes tracking and monitoring the execution of maintenance activities. The maintenance team can register their tasks in the system, monitor work progress, and perform activities in order of priority. -
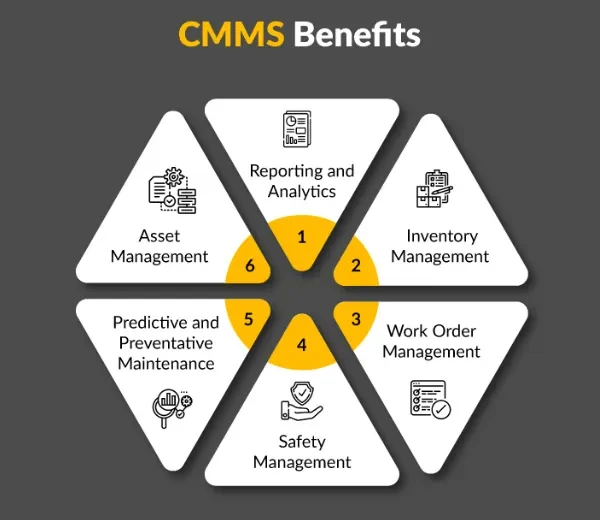
Reporting and Analysis:
The CMMS has the capability to generate reports regarding maintenance activities. These reports can include machine performance, repair scheduling, parts consumption, and other useful information. Additionally, by analyzing these reports, common problems and possible optimizations can be identified.
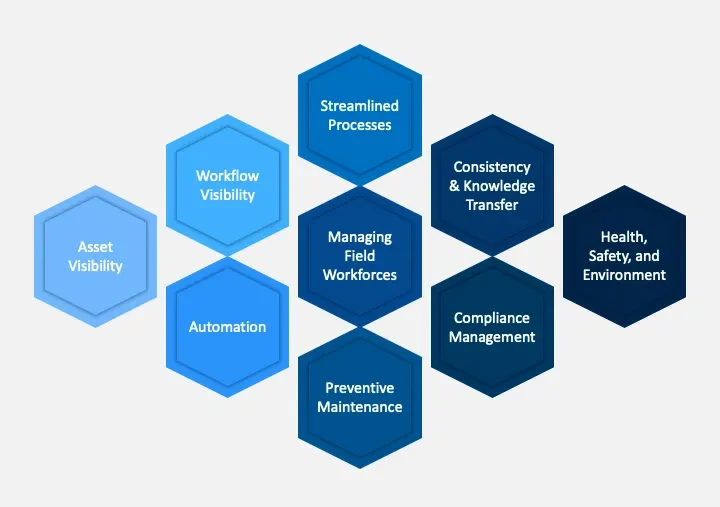
The CMMS can improve machine performance, increase productivity, reduce failures, and optimize repair scheduling. It also helps in reducing costs, improving parts utilization, and managing resources. The applications of CMMS span across various industries, including manufacturing, transportation, energy, and public services, helping organizations effectively manage their assets.
What should be considered when choosing a maintenance management system?
Choosing a maintenance system is important, and you should pay attention to the following:
-
Your Needs and Requirements:
Before selecting a system, carefully examine your needs and requirements. This includes operational needs, expectations regarding capabilities and features, necessary features for your machinery, as well as the level of flexibility and ease of use of the system. -
Compatibility with Machinery:
Ensure that the system has the capability to connect and integrate with your machinery. Check whether the system can connect and transfer information with your existing machinery and has the ability to gather relevant data. -
Features and Capabilities:
Check whether the system has the necessary features and capabilities for your needs. You might need scheduling, activity tracking, notifications, and reporting. Also, consider whether the system has the ability to expand and customize to fit your future needs.


-
Ease of Use:
The system should be designed for easy and practical use. Check whether the user interface is simple and understandable and whether you need extensive training to use it. -
Support and Updates:
Ensure that the system provider offers strong support and provides regular updates and software improvements. Also, check whether sufficient documentation and training resources are available for using the system. -
Security:
Ensure that the system has strong security measures. This includes data protection, limited access to sensitive information, and support for encryption and network security.
In designing the Smart Solution system, an effort has been made to ensure that the product primarily meets your needs and empowers you in maintaining and repairing machinery.
Types of Maintenance in CMMS
The CMMS supports various types of maintenance, each with its specific applications:
-
Corrective Maintenance:
This type of maintenance is performed after a failure occurs and includes immediate repairs to restore machinery to operational status. -
Preventive Maintenance:
Scheduled maintenance to prevent failures, such as replacing parts at specified intervals. -
Predictive Maintenance:
Using data and sensors to predict failures before they occur, which integrates with modern technologies like IoT.
Increasing Profitability
Using a maintenance and repair system can directly and indirectly contribute to increased profitability. The benefits of CMMS in this regard include cost reduction and increased efficiency. Here are some reasons for this:
-
Reducing Failures and Downtime:
Using the maintenance and repair system ensures that maintenance activities are performed regularly and systematically. This means reduced unexpected failures and unplanned downtime of machinery. With fewer stoppages and increased productivity, machine performance improves, leading to increased production and reduced losses. -
Improved Repair Scheduling:
The maintenance and repair system allows you to carry out repairs based on optimal scheduling. This means avoiding premature repairs as well as loss of production time and revenue. With precise scheduling, you can repair machines at the right times while minimizing adverse effects. -
Better Utilization of Parts and Material Consumption:
Using the maintenance and repair system optimizes the management of parts needed for maintenance and repairs. This means better utilization of parts and material consumption, which reduces costs and increases profitability.
-
Improved Machine Performance:
The maintenance and repair system, with the help of systematic planning and timely repairs, ensures improved machine performance and efficiency. With better performance, machines generally have higher productivity, leading to increased output and reduced additional costs. -
Improved Labor Utilization:
By using the maintenance and repair system, repairs and maintenance become improved and planned. This means increased labor productivity. Maintenance personnel can perform their tasks more effectively using system information. -
Data Analysis and Utilization of Statistics:
The maintenance and repair system can provide comprehensive information about machine performance and maintenance activities. By analyzing data and utilizing statistics, you can identify patterns, common problems, and possible optimizations that can impact performance improvement and cost reduction.
Overall, the maintenance and repair system improves performance, productivity, optimal resource utilization, and cost reduction, which directly contributes to increased profitability.
Improving Condition
Machine maintenance and repair ensure their condition in various aspects. The benefits of CMMS in improving condition include increased safety and quality. Here are some of these improvements:
-
Better Performance:
Regular and appropriate maintenance and repair of machines lead to improved performance. This process includes replacing worn parts, making necessary adjustments, cleaning, and fixing technical issues. By performing these activities, machines generally have higher productivity and better performance. -
Increased Useful Life:
Regular maintenance and repairs add to the useful life of machines. By adhering to manufacturer instructions, replacing worn parts, fixing premature failures, and cleaning machines, their useful life can be significantly extended. -
Reduction of Unplanned Downtime:
With the implementation of regular maintenance and repairs, unexpected failures and unplanned downtimes of machines are minimized. This means reduced downtime durations, production delays, and reduced economic losses. -
Improved Safety:
Regular repairs and maintenance of machines play a crucial role in improving employee safety. By eliminating hazards and technical issues, preventing accidents, and improving working conditions, the safety of staff working with the machines is enhanced.
-
Cost Reduction:
Conducting timely maintenance and repair reduces costs associated with failures and unplanned downtimes. Furthermore, by optimizing parts usage and reducing replacement and material consumption costs, it is possible to lower maintenance and repair expenses. -
Improved Production Quality:
Machines in better condition and optimal performance deliver higher quality production. By utilizing the maintenance and repair system and making precise adjustments, product quality can be improved, resulting in more satisfied customers. -
Improved Labor Productivity:
Regular maintenance and repairs of machines enhance labor productivity. With machines operating optimally and minimal downtime, workers can carry out their tasks without interruption and at higher productivity.
Considering these improvements, machine maintenance and repair directly lead to enhanced efficiency, productivity, cost reduction, and increased profitability.
Future Developments of CMMS
With advancements in technology, CMMS are evolving. Future developments include integrating artificial intelligence (AI) for predicting failures, mobile access for remote management, cloud solutions for data storage, the Internet of Things (IoT) for real-time monitoring, and advanced data analysis for better decision-making. These trends will steer CMMS toward predictive and smart maintenance by 2025 and beyond, increasing efficiency.


