If you have ever dealt with organizational processes and automation, you have definitely heard the term BPMN. But what exactly is BPMN and why is it so important in the field of Business Process Management (BPM)? In this article, we will provide a complete guide to BPMN 2.0, introduce its standard symbols, and explain how to model processes with practical examples.
BPMN creates a common language between analysts, managers, and developers to design complex processes graphically and understandably.
What is BPMN?
BPMN stands for Business Process Model and Notation. This language was developed by the OMG organization and introduced as an international standard in version BPMN 2.0 for designing business processes. The goal of BPMN is to create a common understanding among different teams within an organization regarding how processes are executed.
In fact, BPMN is a tool that allows us to visualize business processes in the form of diagrams and clearly see the relationships between roles, activities, and data.
Why is BPMN important?
In today's complex world, organizations need to have a precise understanding of their processes to increase efficiency and reduce errors. BPMN acts as a bridge between business analysts and technical teams, preventing redundancy.
- Increased transparency in organizational processes
- Standardization of modeling methods across the organization
- Facilitation of process implementation in BPMS systems
- Reduction of costs and time for process analysis
In the system of assemblies and contracts projects, BPMN is also used for accurate modeling of decision-making processes, workflow of approvals, and contract approval cycles.
Main components in BPMN 2.0
In version BPMN 2.0, there are four main categories of elements for modeling processes:
- Flow Objects: including Events, Activities, and Gateways
- Connecting Objects: including Sequence Flows, Message Flows, and Associations
- Swimlanes: for differentiating roles and organizational units
- Artifacts: such as annotations, data, and groupings
Using these components, a complete process can be modeled from start to finish. Below are some simple examples of commonly used BPMN symbols.
Commonly Used BPMN Symbols
| Symbol | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 🔵 | Start Event | The starting point of the process, indicating the commencement of activities. |
| ⚪ | End Event | The endpoint of the process, indicating completion of tasks or the final decision. |
| ⬜ | Task | An activity or task that must be performed by a user or system. |
| 🔀 | Gateway | A decision point or branching in the flow (like an if/then condition). |
| ➡️ | Sequence Flow | Indicates the direction of movement between activities and events. |
In BPMS Workflow software, these symbols can be graphically drawn and linked with business rules so that processes can be executed automatically.
Practical Example of Modeling with BPMN
Suppose there is a process for “Requesting Equipment Purchase” in an organization. This process includes the following steps:
- Starting with a purchase request from the requesting unit
- Inventory and budget review by the finance unit
- Sending for CEO approval
- Issuing a purchase order and registering it in the contract system
In the BPMN model, these steps are represented with Start Event, Tasks, Gateways, and End Event symbols. Then by defining business rules in the workflow engine (Workflow Engine), the process will be executed automatically.
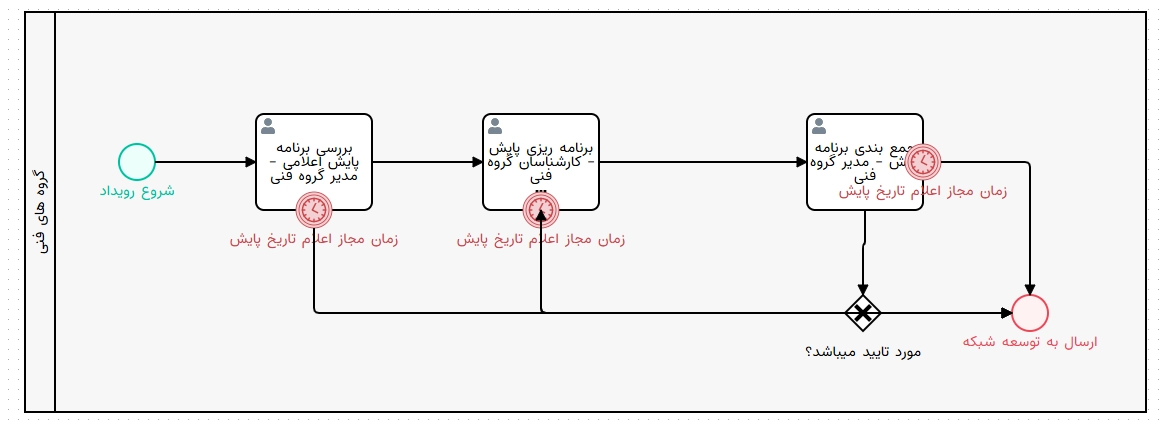
BPMN diagram example for modeling the organizational purchase process
Advantages of Using BPMN in Organizations
- Increased coordination between business and IT teams
- Reduced ambiguity in process documentation
- Direct usability of models in BPMS software
- Lower costs for process analysis and redesign
- Support for analysis and continuous improvement in the BPM cycle
Conclusion
Now that we understand what BPMN is and how it helps in process modeling, we can conclude that this standard language is one of the key tools for successful implementation of Business Process Management (BPM). By understanding the BPMN 2.0 symbols and continually practicing diagram drawing, a more accurate analysis of processes can be provided, and a suitable infrastructure for organizational automation can be created.
Frequently Asked Questions
BPMN is a global standard language for modeling business processes, while a flowchart merely displays a simple sequence of steps.